
 Offers
Offers-
 Account
Account
-
0
 Favorite
Favorite
-
0
 Basket
Basket



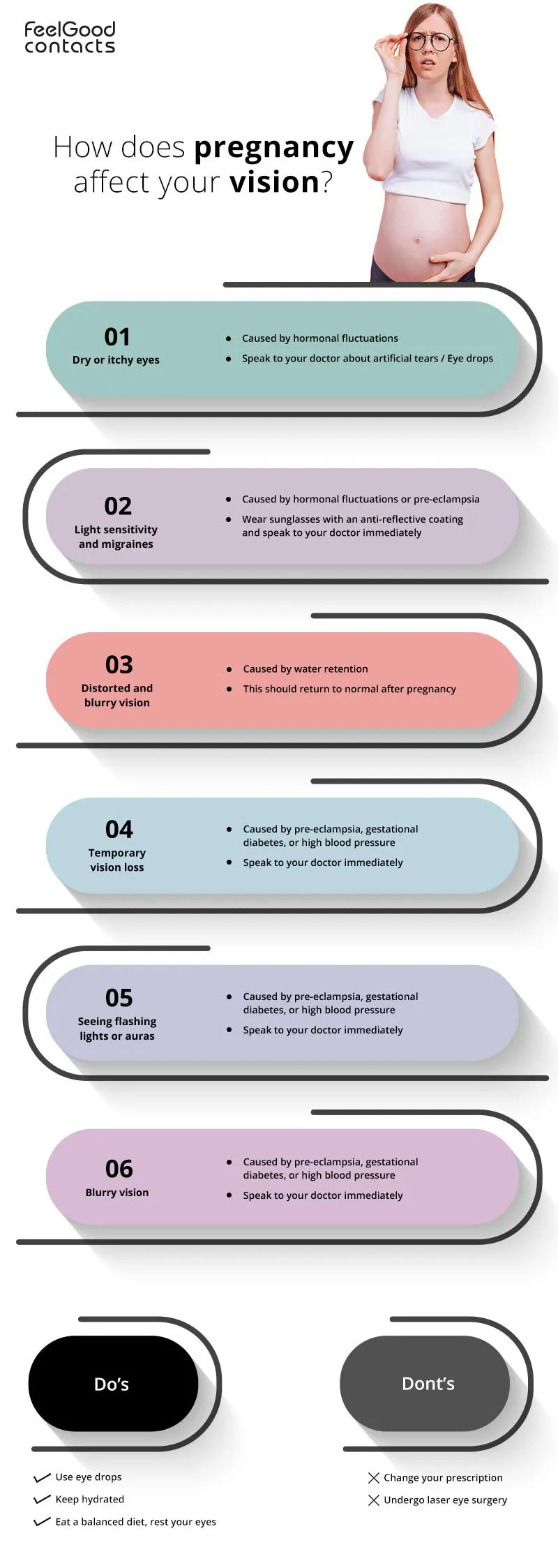
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings about a multitude of changes in a woman's body, and surprisingly, one area that is often affected is vision. The hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can lead to physiological changes in the eyes and visual system. While many of these changes are temporary, expectant mothers must be aware of what is considered normal and when to seek medical attention.
Pregnancy can impact your eyesight because of the hormonal, metabolic, fluid retention, and blood circulation changes. If you have any pre-existing conditions such as diabetic eye disease, these changes may increase vision issues. Reduced tear production during pregnancy can lead to dry eyes or itchy eyes or general discomfort for contact lens wearers. Artificial tears or hydrating eye drops can help but it is highly recommended to consult your doctor or optician if you experience any of these issues. Try our comfi Soothe Drops to ease the irritation caused by dry eyes.
Wondering whether you are having dry eyes or not? Take our dry-eye quiz to find out.
During pregnancy, your eye’s sensitivity to light could also increase and may cause migraines. Sunglasses with UV protection and anti-reflective coating can be worn whilst outdoors to reduce headaches.
Distorted and blurry vision is also common during pregnancy due to water retention. This can result in water building up behind the eye and causing the cornea to change shape. These changes are usually temporary. Corrective eye surgery is not recommended during pregnancy as it would be impossible to accurately measure the cornea.
Yes, it’s completely normal to have some eye problems during pregnancy. While pregnancy-induced vision changes are often temporary, expectant mothers need to differentiate between normal shifts and potential signs of underlying issues. Regular eye check-ups and open communication with a healthcare professional can ensure any concerning changes are addressed promptly, safeguarding both maternal health and the well-being of the developing child.
There are many changes that occur in the body during pregnancy that may lead to changes in vision. Some of these changes are:
The ocular effects of pregnancy can involve various parts of the eye, leading to shifts in vision. However, most of these changes are temporary and tend to resolve postpartum or after breastfeeding. Common physiological changes include fluctuations in corneal thickness, dry eyes, and changes in intraocular pressure.
Pregnancy hormones can cause fluid retention, which causes the cornea to thicken and the fluid pressure within the eyeball to increase. This may result in blurred vision. Additionally, pregnancy hormones can decrease tear production, and lead to dry eyes.
A serious condition that can affect some pregnant women, usually after the 20th week of pregnancy. Characterised by a combination of high blood pressure and protein in urine, it leads to visual disturbances, such as blurry vision or light sensitivity.
For most women, normal vision returns within a few weeks or months after delivery. It is advisable to have a comprehensive eye exam after pregnancy to check your eye health and vision and to update your prescription if needed.
If you experience changes in your vision or any eye problems during your pregnancy or post-pregnancy, you should consult your optician or doctor for advice.
Disclaimer: The advice in this article is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical care or an in-person check-up. Please check with an eyecare professional before purchasing any products or remedies. For information on our article review process, please refer to our Editorial Policy.